String类
- Java中的String类是一个不可变的字符串类型。属于引用类型,由于String对象是不可变的,所以每次对字符串进行操作时都会创建新的String对象
构造方法
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String() | 创建空白的字符串 不包含任何内容 |
| public String(String original) | 根据传入的字符串 创建字符串对象 |
| public String(char[] chs) | 根据字符数组 创建字符串对象 |
| public String(byte[] chs) | 根据字节数组 创建字符串对象 |
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "阿乐的小屋";
String s1 = new String("阿乐的小屋");
String s2 = new String();
//传递一个字符数组 将数组转换为字符串对象
char [] chs = {'a','b','c'};
chs[0] = 'z';
String s3 = new String(chs); //zbc
//传递一个字节数组 将数组转换为字符串对象
byte [] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101};
bytes[0] = 90;
String s4 = new String(bytes); //Zbcde
}
}String内存分析
- 在使用双引号直接赋值的时候,系统会检查字符串在字符串常量池中是否存在 不存在就创建新的 存在了就复用 所以str = str1
- 使用String构造方法new String创建两个对象 那么这两个对象在内存上地址是不相同的
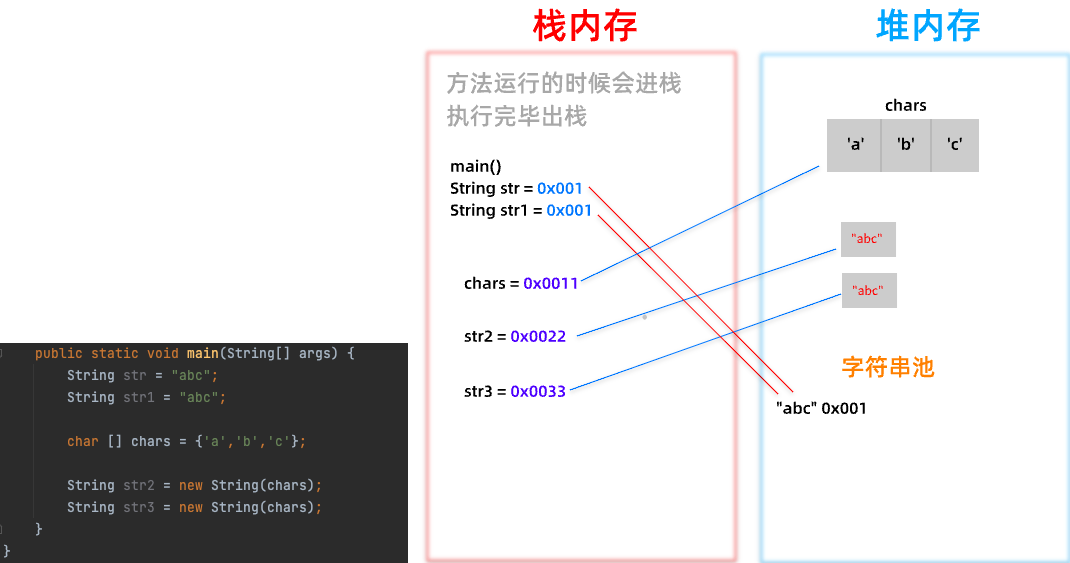
字符串的比较
public class StringDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "blgodx.com";
String s1 = "Blgodx.com";
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
// == 如果是基本类型 比较的是数据值 如果是引用类型比较的地址值
System.out.println(s == s1); //true
//比较字符串是否相同
System.out.println(s.equals(s1)); //true
//忽略大小写进行比较
System.out.println(s.equalsIgnoreCase(s1));
//以下使用的==进行比较两个对象内存地址 由于Scanner是在栈内存中创建的 而str1是在堆内存中创建的 所以两个地址并不相同
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入一个字符串:");
String str = scan.next();
String str1 = "abc";
System.out.println(str == str1);
}
}String常用方法
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public boolean isEmpty() | 判断是否为空 |
| public boolean startsWith(String prefix) | 判断字符串以什么开头 |
| public boolean endsWith() | 判断字符串以什么结尾 |
| public String toUpperCase() | 将字符串小写转换为大写 |
| public String toLowerCase() | 将字符串大写转换为小写 |
| public char charAt() | 查找索引输出字符串 |
| public int indexOf(String str) | 查找字符串输出索引下标 |
| public int lastIndexOf() | 查找最后一个字符串的下标 |
| public String substring(int beginindex) | 从下标起始位置截取到结束 |
| public String substring(int beginindex,int beginendindex) | 从起始下标到结束下标截取字符串 |
| public String trim() | 去除字符串中的空格 |
| public String replace(char old Char,char newChar) | 将旧的字符替换为新的 |
public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "blogdxm.com";
System.out.println(str.isEmpty()); //是否空 false
System.out.println(str.startsWith("b")); //判断是否以b开头 true
System.out.println(str.endsWith("m")); //判断是否以m结尾 true
System.out.println(str.toUpperCase()); //将字符串转换为大写
System.out.println(str.toLowerCase()); // 将字符串转换为小写
System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); //打印0索引 b
System.out.println(str.indexOf("m")); //查找m的下标 6
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("m")); //查找m的最后一个下标 10
System.out.println(str.substring(1)); //从下标1开始截取字符串并打印 logdxm.com
System.out.println(str.substring(0,5)); //从下标0开始到5结束打印字符串 blogd
System.out.println(str.replace('b', 's')); //将字符b替换为s
}
}作业练习
- 获取键盘输入结尾是.jpg或者.png结尾 如果不是则打印错误信息 如果是则声称一个uuid 将uuid和获取到的文件类型拼接在一起输出
public class StringDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入.jpg结尾或者.png结尾的名字:");
String str = scan.next();
if (!str.endsWith(".png") && !str.endsWith(".jpg")){
System.out.println("输入错误请重新输入");
}else {
//获取最后一个.
int find = str.lastIndexOf(".");
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
//从.开始截取到最后 输入123.d.jpg 会直接截取.jpg
String pic = str.substring(find);
//打印内容
System.out.println(uuid + pic);
}
}
}- 定义一个数组里面存放违规的字 获取用户输入 如果输入的内容包含数组中的内容将文本替换为*并且打印到控制台
public class StringDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("文明用语 人人有责:");
String input = scan.next();
char [] chars = {'死','傻','逼','草','操'};
for (char aChar : chars) {
input = input.replace(aChar,'*');
}
System.out.println(input);
}
}StringBuffer
- StringBuffer()构造一个空的字符串缓冲区,并且初始化为 16个字符的容量。
- StringBuffer(int capacity);构造一个没有字符的字符串缓冲区和指定的初始容量。
- StringBuffer(String str);构造一个初始化为指定内容的字符串缓冲区。
- StringBuffer:可以给 可以不给 不给的情况下回自动扩容
- 线程安全 线程安全 线程安全 适用多线程
使用场景为频繁拼接 反转。
public class StringDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个空的字符缓冲区。底层创建16个字符的容量
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
//定义一个含有10个字符容量的字符缓冲区
StringBuffer sb1 = new StringBuffer(10);
//capacity 容量大小
int capacity = sb.capacity();
System.out.println(capacity);
//追加字符
sb.append(1);
sb.append("阿乐的小屋");
sb.append(true);
//这里的sb是StringBuffer类型 通过tostring方法转换为String类型
String str = sb.toString();
//转换为String类型调用substring 进行截取字符串
System.out.println(str.substring(1,6));
//反转字符串reverse
StringBuffer reverse = sb.reverse();
System.out.println(reverse);
}
}StringBuffer和StringBuilder区别
- StringBuffer的方法都是同步的 StringBuilder方法是非同步的
- StringBuffer 线程安全 使用于多线程
- StringBuilder 线程不安全 适用于单线程 在单线程环境下比StringBuffer更快