IO流
File类的常用方法
- File file = new file("路径的名称");
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| getAbsoluteFile | 获取绝对路径 |
| getPath | 获取路径 |
| getName | 获取名称 |
| getParent | 获取上一层的目录 |
| length | 获取长度 |
| lastModified | 获取最后一次修改的时间 |
| list | 获取目录下的文件或文件名 |
| listFiles | 获取目录下的文件或文件名返回绝对路径 |
| renameTo | 剪切+粘贴 |
示例:
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//在内存方面上
File file = new File("Hello.txt"); //相对路径 在当前的工程下创建Hello.txt
File file1 = new File("D:\\Demo\\untitled\\src\\Day02\\File\\Hi.txt"); //绝对路径
System.out.println("绝对路径是:" + file.getAbsoluteFile());
System.out.println("路径是:" + file.getPath());
System.out.println("名称是:" + file.getName());
System.out.println("上一层的文件目录为:" + file.getParent()); //若无上层目录返回为NULL
System.out.println("长度为:" + file.length());
System.out.println("获取最后一次修改的时间为:" + new Date(file.lastModified()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("绝对路径是:" + file1.getAbsoluteFile());
System.out.println("路径是:" + file1.getPath());
System.out.println("名称是:" + file1.getName());
System.out.println("上一层的文件目录为:" + file1.getParent()); //若无上层目录返回为NULL
System.out.println("长度为:" + file1.length());
System.out.println("获取最后一次修改的时间为:" + file1.lastModified());
System.out.println();
show();
System.out.println();
add();
}
public static void show(){
//输出这个目录下的文件和文件名
File file = new File("D:\\Program Files (x86)\\Tencent");
String[] list = file.list();
for (String s : list) {
System.out.println("获取到的目录为:" + s);
}
System.out.println();
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
System.out.println("获取到的绝对路径为:" + f);
}
}
public static void add(){
File file = new File("Hello.txt");
File file1 = new File("D:\\Demo\\untitled\\src\\Day02\\File\\Hi.txt");
//file必须存在 file1 不可以存在 这个操作相当于是将Helo.txt 剪切 到D\\Demo\\untitled\\src\\Day02\\File目录 在粘贴为Hi.txt
//linux表示:mv D/Demo/untitled/Hello.txt /D/Demo/untitled/src/Day02/File/hi.txt 移动+重命名
boolean b = file.renameTo(file1);
System.out.println(b);
}
}运行结果:
绝对路径是:D:\Demo\untitled\Hello.txt
路径是:Hello.txt
名称是:Hello.txt
上一层的文件目录为:null
长度为:5
获取最后一次修改的时间为:Wed Dec 21 16:13:40 CST 2022
绝对路径是:D:\Demo\untitled\src\Day02\File\Hi.txt
路径是:D:\Demo\untitled\src\Day02\File\Hi.txt
名称是:Hi.txt
上一层的文件目录为:D:\Demo\untitled\src\Day02\File
长度为:0
获取最后一次修改的时间为:0
获取到的目录为:TIM
获取到的目录为:WeChat
获取到的绝对路径为:D:\Program Files (x86)\Tencent\TIM
获取到的绝对路径为:D:\Program Files (x86)\Tencent\WeChat
TrueFile类的判断创建删除
- 判断:返回为boolean类型
| 属性 | 方法 |
|---|---|
| isDirectory | 判断是否是文件目录 |
| isFile | 判断是否是文件 |
| exists | 判断是否存在 |
| canRead | 判断是否可读 |
| canWrite | 判断是否可写 |
| isHidden | 判断是否隐藏 |
public class FileTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用图形化界面在这个目录创建一个likedx.txt文件
File file = new File("D:\\Demo\\untitled\\src\\Day02\\File\\likedx.txt");
System.out.println("判断是否是文件目录:" + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("判断是否是文件:" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("判断是否存在:" + file.exists());
System.out.println("判断是否可读:" + file.canRead());
System.out.println("判断是否可写:" + file.canWrite());
System.out.println("判断是否隐藏:" + file.isHidden());
System.out.println();
File file1 = new File("D:\\Demo");
System.out.println("判断是否是文件目录:" + file1.isDirectory());
System.out.println("判断是否是文件:" + file1.isFile());
System.out.println("判断是否存在:" + file1.exists());
System.out.println("判断是否可读:" + file1.canRead());
System.out.println("判断是否可写:" + file1.canWrite());
System.out.println("判断是否隐藏:" + file1.isHidden());
}
}- 创建和删除:返回为boolean类型
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| createNewFile | 创建文件 |
| mkdir | 普通创建文件夹 |
| mkdirs | 覆盖创建文件夹 |
| delete | 删除文件或者文件夹不会经过回站 |
public class FileTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//存在了就不创建
File file = new File("D:\\Demo\\untitled\\src\\Day03");
//不管存在不存在直接覆盖创建一个文件夹
File file1 = new File("D:\\Demo\\untitled\\src\\Day03\\Day04");
//linux下的mkdir
//不存在就创建文件夹: mkdir D/Demo/untitled/src/Day03
//不存在就覆盖创建文件夹:mkdir -p D/Demo/untitled/src/Day03/11
System.out.println(file.mkdir());
System.out.println(file1.mkdirs());
//如果Day03下的Day04存在 那就删除新创建的src下的03和04
if (file1.exists()) {
file1.delete();
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}
}public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
add();
show();
}
//创建文件
public static void add() {
File file = new File("D:\\likedx.txt");
try {
//不存在就创建 存在就给个提示
if (file.createNewFile()){
System.out.println("文件已存在");
}else {
System.out.println("文件已创建");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); //打印错误信息
}
}
//D盘中是否包含png文件 如果包含就打印出来
public static void show(){
File file = new File("D:\\");
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f: files) {
String name = f.getName();
if (name.endsWith("png")) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
}IO流框架
| 分类 | 字节输入流 | 字节输出流 | 字符输入流 | 字符输出流 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抽象基类 | InputStream | OutputStream | Reader | Writer |
| 访问文件 | FileInputStream | FileOutputStream | FileReader | FileWriter |
| 访问数组 | ByteArrayInputStream | ByteArrayOutputStream | CharArrayReader | CharArrayWriter |
| 访问管道 | PipedInputStream | PipedOutputStream | PipedReader | PipedWriter |
| 访问字符串 | StringReader | StringWriter | ||
| 缓冲流 | BufferedInputStream | BufferedOuputStream | BufferedReader | BufferedWriter |
| 转换流 | InputStreamReader | OutputStreamWriter | ||
| 对象流 | ObjectInputStream | ObjectOutputStream | ||
| FilterInputStream | FilterOutputStream | FilterReader | FilterWriter | |
| 打印流 | PrintStream | PrintWriter | ||
| 推回输入流 | PushbackInputStream | PushbackReader | ||
| 特殊流 | DataInputStream | DataOutPutStream |
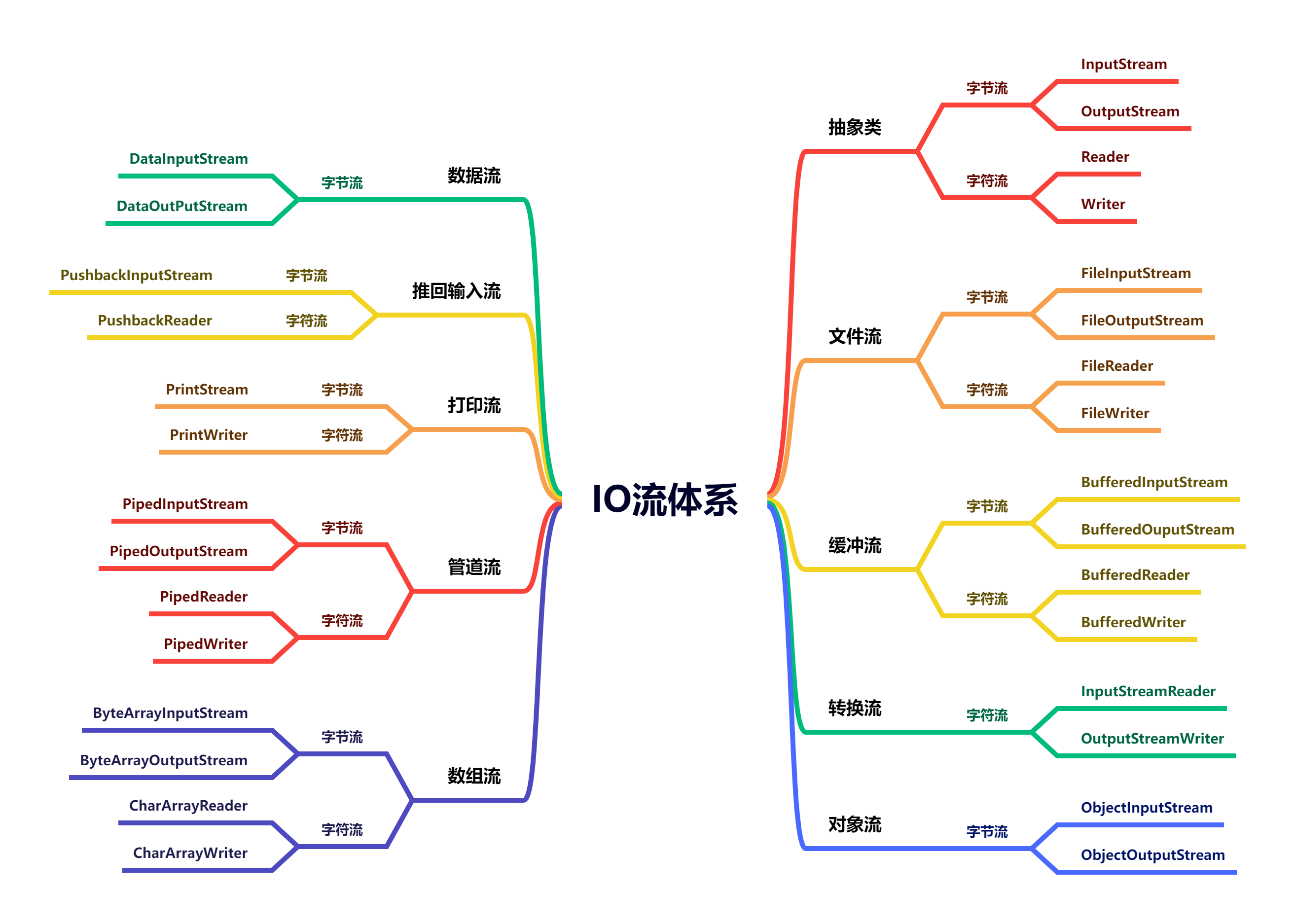
什么是IO流?
存储和读取数据的解决方案
- input(输入) output(输出) 数据就像水流一样进行传输
IO流的作用
- 用于读写数据(本地文件,网络)
IO流按照流向可以分类哪两种流
- 输出流:程序---->文件
- 输入流:文件---->程序
IO流按照操作文件的类型可以分类哪两种流
- 字节流:可以操作所有类型的文件
- 字符流:只能操作纯文本的文件
什么是纯文本的文件
- txt md xml lrc json .....
文件流
字节流
字节输出流FileOutputStream
- 操作本地文件的字节输出流 可以把程序的数据写到本地文件中
- 每次只能操作一个字节
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| write(int b) | 一次写一个字节数据 |
| write(byte[] b) | 一次写一个字节数组数据 |
| write(byte []b, int off, int len) | 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 |
public class FileTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
//在原有基础上追加写入数据
//FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("a.txt",true);
fos.write(97); //a
//换行
String s = "\n";
byte[] bytes2 = s.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes2);
byte[] bytes = {97,98,99,100,101}; //abcde
//写入数据 一次性写进去byte数组
fos.write(bytes);
//换行操作
String s1 = "\n";
byte[] bytes3 = s.getBytes();
fos.write(bytes3);
byte[] bytes1 = {103,104,105,106,107,108};
//从0索引开始写进两个数据进去
fos.write(bytes1,0,2);
//关闭流
fos.close();
}
}字节输入流FileInputStream
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| read(byte[] b) | 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节 |
| read(byte[] b,int off,int len) | 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组 |
- 操作本地文件的字节输入流,可以把本地文件中的数据读取到程序中来
public class FileTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建流 如果文件不存在直接报错
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src\\Demo3\\likedx.txt");
int read;
//读取数据
//把读取到的结果赋给read 然后在打印出来 如果读到文件末尾会返回-1
while ((read = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) read);
}
//关闭流
fis.close();
}
}- 拷贝文件
public class FileTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\IO.png");
//创建拷贝对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\Demo3\\copy.png");
//拷贝文件
int len;
while (((len = fis.read()) != -1)){
fos.write(len);
}
//关闭流
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}public class FileTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\IO.png");
//创建拷贝对象
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("src\\Demo3\\copy.png");
//拷贝文件
//创建一个byte类型的数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
while (((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1)){
//上面读取多少就写多少
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//关闭流
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}字符流
字符输入流FileReader
- 字符流的底层就是字节流
特点
- 输入流:一次读一个字节,遇到中文时一次多多个字节
- 输出流:底层会把数据按照指定的编码方式进行编码 变成字节在写入文件中
- 对纯文本文件进行读写操作
public class FileTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("1.txt");//北国风光 千里冰封 万里雪飘
int len;
//read读取的内容转换为10进制 gbk一次读两个字节 utf8一次三个字节 如果想看到中文汉字 用char进行强制转换
while ((len = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) len);
}
//关闭流
fr.close();
}
}public class FileReaderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("1.txt"); //北国风光 千里冰封 万里
//读取数据 这里使用的char数组而不是byte数组
char[] chars = new char[2];
int len;
//read:读取数据 进行解码 强制转换为中文
while ((len = fr.read(chars))!= -1) {
//把数组中的数据变成字符串进行打印
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,2));
//北国 风光 千 里冰 封 万里
}
//关闭流
fr.close();
}
}字符输入流原理
底层创建字符输入流对象。并创建缓冲区(长度为8192字节数组)
- 读取数据 判断缓冲区是否有数据可读
- 缓冲区没有数据:就从文件获取数据装到缓冲区中,每次尽可能装满缓冲区 如果文件中没有数据了就返回-1
- 缓冲区有数据:就从缓冲区中读取
字符输出流FileWriter
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| write(int c) | 写出一个字符 |
| write(String str) | 写出一个字符串 |
| write(String str, int off, int len) | 写出一个字符串的一部分(off = 下标开始 -->len 写出几个字符) |
| write(char[] cbuf) | 写出一个字符数组 |
| write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 写出字符数组的一部分(off = 下标开始 -->len 写出几个字符) |
public class FileWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建流 在文件中追加数据
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("1.txt");
//写出一个字符
fw.write(97);
String s = "\r\n";
fw.write(s); //a
//写出一个字符串
String str = "我的博客";
fw.write(str); //我的博客
fw.write(s);
//写出一个字符串的一部分 从下标1开始 写入bc
fw.write("abcde",1,2); //bc
fw.write(s);
//写出一个字符数据
char[] chars = {'l','i','k','e','d','x','.','c','o','m'};
fw.write(chars); //likedx.com
fw.write(s);
//写出数组的一部分
fw.write(chars,0,2); //li
//关闭流
fw.close();
}
}字符输出流原理
底层创建字符输出流对象。并创建缓冲区(长度为8192字节数组)
- 写出数据 缓冲区装满了或者有数据会自动刷新后并写出数据到文件中
- flush 手动刷新 刷新完毕还可以继续写出数据
- 如果关闭流,无法往文件中写出数据
缓冲流
字节流
字节缓冲输入流BufferedInputStream
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| read(byte[] b) | 从输入流中读取一定数量的字节 |
| read(byte[] b,int off,int len) | 将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入 byte 数组 |
public class FileTest09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建输入流进行读入数据
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("1.txt"));
//创建输出流进行写出数据
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy.txt"));
//长度
int len;
while ((len = bis.read())!= -1) {
bos.write(len);
}
//关闭流
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}字节缓冲输入流BufferedOutputStream
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| write(int b) | 一次写一个字节数据 |
| write(byte[] b) | 一次写一个字节数组数据 |
| write(byte []b, int off, int len) | 一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 |
public class FileTest09 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建输入流进行读入数据
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("1.txt"));
//创建输出流进行写出数据
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("copy.txt"));
//创建一个1024字节的数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
//长度
int len;
//读入一次讲数据存储到数组当中
while ((len = bis.read(bytes))!=-1) {
bos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//关闭流
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}字节缓冲流原理

字符流
字符输入流BufferedReader
| 字符缓冲输入流特有方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public String readLine() | 读取一行数据 如果没有数据可读了,会返回null |
| 字符缓冲输出流特有方法 | 说明 |
| public void newLine() | 写出回车到文件中 |
public class FileTest10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("1.txt"));
//读取一行就换行 不会把回车读取到内存中
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
br.close();
}
}字符输出流BufferedWriter
public class FileTest11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("1.txt",true));
bw.write("我是一只小可爱");
//写出回车到文件中
bw.newLine();
bw.close();
}
}缓冲流有哪几种?
- 字节缓冲输入流:BufferedInputStream
- 字节缓冲输出流:BufferedOutputStream
- 字符缓冲输入流:BufferedReader
- 字符缓冲输出流:BufferedWriter
缓冲流为什么能提高性能?
- 缓冲流自带长度为8192的缓冲区
- 可以显著提高字节的读写性能
- 对于字符流提升不明显,对于字节缓冲流而言关键是两个特有的方法
字符缓冲流特有的是哪两个方法?
- 字符缓冲输入流BufferedReader:readerLine()
- 字符缓冲输出流BufferedWriter:newWriter()
作业练习
- 将一个文本中的内容在前面添加数字对每一行内容进行排序
public class FileDemo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//123.txt用来存储没有排序的文本内容 456.txt为写出后的内容
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\123.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\456.txt"));
String data;
//定义一个计数器
int count = 1;
while ((data = br .readLine()) != null) {
String s = count + "." + data;
//写入的格式为1. 到文本结束
bw.write(s);
//换行
bw.newLine();
//计数器+1
count++;
}
//原内容
//文本内容
//文本内容
//排序后
//1.文本内容
//2.文本内容
//3.文本内容
//关闭流
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}将一个文本中的内容文章顺序进行恢复到一个新的文件中
实现原理:
- 使用字符缓冲输入流(BufferedReader)读取文本内容
- 将文本的内容进行分割用数组存储 把分割好的内容存储到集合(TreeMap)当中 获取key和value
- 使用字符缓冲输出流(BufferedWriter)进行写出数据。遍历集合中的key和value 用缓冲流写出到文本
- 注意:在写出文本到文件中需要用到一个特有的方法newLine 写出一行自动进行回车
public class FileTest11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("1.txt"));
String len;
//创建一个集合用来添加数组中的数据
TreeMap<Integer,String> tm = new TreeMap<>();
//读取内容 创建一个数组将内容进行切割并存储到数组中
while ((len = br.readLine())!= null) {
String [] arr = len.split("\\.");
//将索引0和1添加到集合中 因为是Integer类型 所以这里0索引要强制转换类型
tm.put(Integer.parseInt(arr[0]),arr[1]);
}
//关闭流
br.close();
//写出文本到文件中
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("2.txt"));
//对集合进行遍历
Set<Map.Entry<Integer, String>> entries = tm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : entries) {
//将遍历的key和value添加到缓冲流中进行写出数据到文本里面去
bw.write(entry.getKey() + "." + entry.getValue());
//每次写出一行进行换行操作
bw.newLine();
}
bw.close();
}
}用字符缓冲流实现一个验证程序次数的小程序
- 当程序运行超过3次提示:软件免费试用3次。欢迎您注册会员后继续使用
程序运行演示如下:
- 第一次运行控制台输出:欢迎使用本软件,第1次使用免费
- 第二次运行控制台输出:欢迎使用本软件,第2次使用免费
- 第三次运行控制台输出:欢迎使用本软件,第3次使用免费
- 第四次运行控制台输出:本软件只能免费使用3次 。欢迎您注册会员后继续使用
public class FileTest12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("1.txt"));
//把文件的数字读取到内存当中
String line = br.readLine();
//字符串转换为包装类
int count = Integer.parseInt(line);
count++;
//判断
if (count<=3){
System.out.println("欢迎使用本软件,第" + count +"次使用免费");
}else if (count>=10) {
System.out.println("检测到您运行次数较多限制使用");
}else {
System.out.println("本软件免费运行3次.请您注册会员后进行使用");
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("1.txt"));
//将自增加之后的count写出到文件中
bw.write(count + "");
bw.close();
}
}转换流
- 将字节流转换为字符流或讲字符流转换为字节流
- 支持设置字符编码、自动刷新缓冲区、解决半个中文字符等问题
字符流(JDK11之前)
- InputStreamReader字符转换输入流
- OutputStreamWriter字符转换输出流
public class FileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("1.txt"),Charset.forName("GBK"));
//读取文本内容输出到控制台
int ch;
while ((ch = isr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char) ch);
}
isr.close();
//将字符串写出到文本当中
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("1.txt"),Charset.forName("GBK"));
osw.write("我爱学习,学习快乐");
osw.close();
}
}字符流(JDK11之后)
FileReader字符输入流
public class FileTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileReader fr = new FileReader("1.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
int ch;
//读取文本内容
while ((ch = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println((char) ch);
}
fr.close();
//利用转换流将字符串写出到文本中
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("1.txt",Charset.forName("GBK"));
fw.write("学习快乐 我爱学Java");
//关闭流
fw.close();
}
}作业练习
- 将GBK格式的文件转换为UTF-8格式的文件
public class FileDemo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// file为源文件 file1为转换UTF-8写出的文件
File file = new File("D:\\123GBK.txt");
File file1 = new File("D:\\123UTF-8.txt");
//造流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//转换输入流指定编码格式
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"GBK");
//转换输出流指定编码格式UTF-8
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file1);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"UTF-8");
//读写过程
char [] chars = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(chars))!= -1) {
osw.write(chars,0,len);
}
//关闭流
osw.close();
fos.close();
isr.close();
fis.close();
}
}对象流(序列化流)
- 可以把java中的对象写入到本地文件当中
学生类Student
public class Student implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
private transient int age;
private int id;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}序列化类ObjectStreamDemo (字节输出流)
public class ObjectStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个文件输出流
FileOutputStream fts = new FileOutputStream("test.txt");
//创建一个对象流
ObjectOutputStream oot = new ObjectOutputStream(fts);
Student stu = new Student("张三",18,1);
Student stu2 = new Student("李四",21,2);
//将对象存储在集合中
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(stu);
list.add(stu2);
//对存储的集合数据进行序列化
oot.writeObject(list);
//关闭流
oot.close();
fts.close();
}
}反序列化类ObjectStreamDemo2(字节输入流)
public class ObjectStreamDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(fis);
//反序列化进行读取
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
//关闭流
fis.close();
ois.close();
}
}- 首先创建一个
Person对象,并使用ObjectOutputStream将其写入到名为person.ser的文件中。然后,使用ObjectInputStream从同一文件中读取该对象,并将其转换为Person类型。
public class ObjectStreamExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义待写入的对象
Person person = new Person("Alice", 25);
// 使用对象输出流将对象写入文件
try (ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("person.ser"))) {
output.writeObject(person);
System.out.println("成功写入对象:" + person);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("写入对象时发生异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
// 使用对象输入流从文件中读取对象
try (ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("person.ser"))) {
Person p = (Person) input.readObject();
System.out.println("成功读取对象:" + p);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IOException e) {
System.out.println("读取对象时发生异常:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
class Person implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + "}";
}
}总结:
- 如果一个对象类的对象能被序列化,那么这个类必须实现一个接口
Serializable 序列化以后再次修改对象类,进行反序列化的时候会出现
InvalidClassException异常- 需要在对象类中添加
erialVersionUID(序列化、版本号)
- 需要在对象类中添加
- 如果一个对象中的某个成员不想被序列化 给成员变量加
transient关键字修饰。关键字标记成员变量不参与序列化过程
打印流
字节打印输出流PrinStream
- 打印流一般是指PrinStream字节输出流,PrintWriter字符输出流两个类
- 打印流只操作文件目的地,不能操作数据源
- 特有的写出方法:可以实现,数据原样输出
- 特有的写出方法:可以实现自动刷新,自动换行
public class PrintTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("1.txt");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(fos,true,Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
ps.println("我爱学习,学习爱我"); //写出数据 自动换行 自动刷新
ps.println(97);
ps.print(true);
ps.println(); //换行
ps.printf("%s爱上了%s","阿珍","阿强"); //%s %s 占位符
//关闭流
ps.close();
fos.close();
}
}字符打印输出流PrintWriter
public class PrintTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("1.txt"));
pw.println("收藏从未停止,学习从未开始");
pw.print(123); //不换行
pw.close();
}
}总结:
- 打印流有字节打印流和字符打印流
- 打印流不能操作数据源 只能操作目的地
- 字节打印流:默认自动刷新。println自动换行
- 字符打印流:自动刷新需要开启。特有的println自动换行
作业练习:
- 获取键盘输入 将输入的英文转换为大写
public class FileDemo13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//获取键盘输入 将字符流包装成缓冲流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = null;
while ((s = br.readLine())!= null) {
System.out.println("----->" + s.toUpperCase());
}
br.close();
}
}